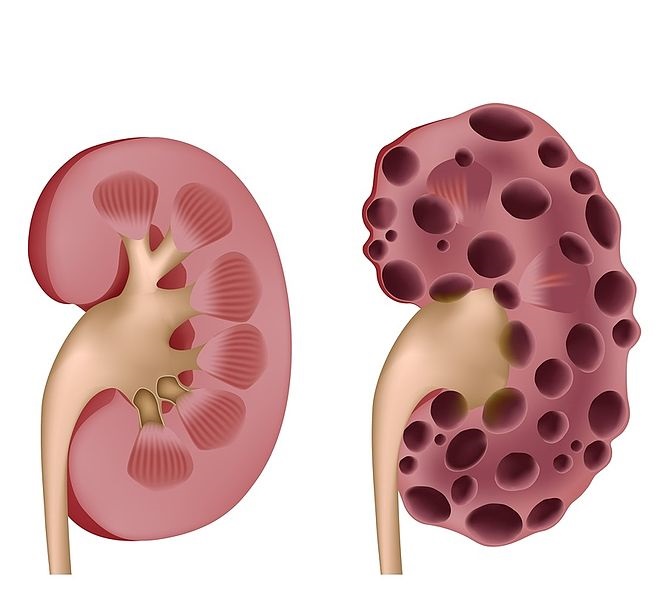
Renal disease, also known as kidney disease, refers to a condition in which the kidneys are damaged and are not able to function properly. The kidneys play an important role in removing waste and excess fluids from the body, regulating blood pressure, and producing hormones that help to maintain healthy bones.
Symptoms
The symptoms of renal disease can vary depending on the stage and type of the condition. In the early stages, symptoms may be mild or absent altogether. As the condition progresses, however, symptoms can become more severe and include fatigue, nausea, swelling in the legs or feet, decreased urine output, and changes in urination frequency or color. In some cases, people with renal disease may also experience high blood pressure, anemia, or bone pain. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, as early detection and treatment can help slow the progression of the disease and prevent complications.
Symptoms of renal disease can vary depending on the stage of the disease, but may include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Decreased urine output or changes in urine color
- Shortness of breath
- High blood pressure
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Difficulty sleeping
- Itchy skin
- Muscle cramps
How to Control Renal Disease
There are several ways to control renal disease and prevent further damage to the kidneys:
1. Manage blood pressure
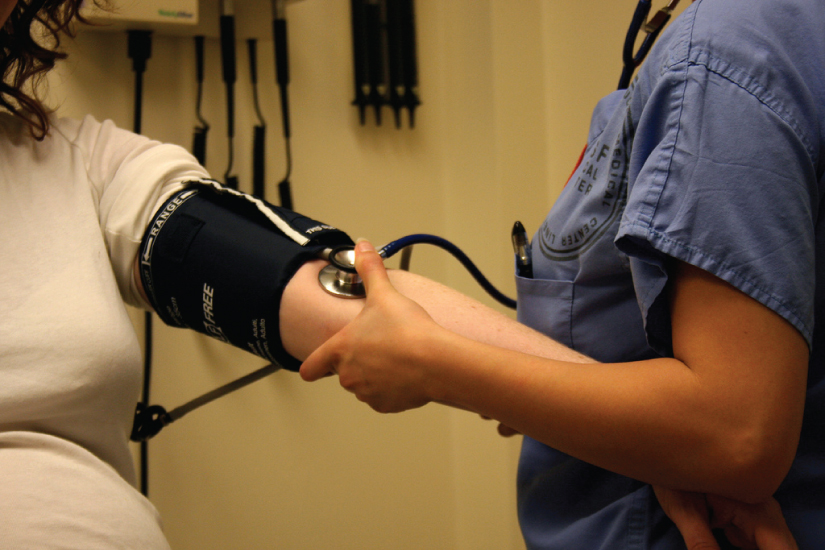
Managing blood pressure is crucial in controlling renal
disease. High blood pressure can damage blood vessels in the kidneys and make
them less effective in removing waste from the body. Healthcare providers may
prescribe medications such as ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers
to help control blood pressure.
2. Manage blood sugar

Managing blood sugar levels is also important in controlling
renal disease. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels in the kidneys,
leading to kidney damage. People with diabetes should work with their healthcare
providers to develop a plan for managing blood sugar levels through diet,
exercise, and medication. Check the renal
diet plan here.
3. Maintain a healthy diet

Maintaining a healthy diet is also important in managing
renal disease. A healthy diet can help ease the workload on the kidneys and
prevent complications associated with the condition. This includes limiting
sodium, protein, and phosphorus intake. A nutritionist for pregnancy can help
develop a healthy meal plan that supports kidney health.
4. Stay hydrated

Staying hydrated is also crucial in managing renal disease.
Dehydration can make it harder for the kidneys to remove waste from the body.
Drinking enough water can help prevent dehydration and support kidney function.
People with renal disease should aim to drink enough water to produce clear or
light yellow urine. However, people with advanced renal disease may need to
limit fluid intake to avoid putting additional strain on the kidneys.
5. Exercise regularly

Regular exercise is important for managing renal disease.
Exercise can help improve cardiovascular health, lower blood pressure, and
reduce the risk of complications associated with the condition. People with
renal disease should aim to engage in moderate exercise for at least 30 minutes
most days of the week. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare
provider before starting an exercise program, especially if there are any other
underlying health conditions.
6. Quit smoking

Regular exercise is important for managing renal disease.
Exercise can help improve cardiovascular health, lower blood pressure, and
reduce the risk of complications associated with the condition. People with
renal disease should aim to engage in moderate exercise for at least 30 minutes
most days of the week. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare
provider before starting an exercise program, especially if there are any other
underlying health conditions.
7. Take medications as prescribed
.jpg)
Medications can help control blood pressure, manage blood
sugar levels, and prevent complications associated with renal disease. It is
important to take medications as prescribed and work closely with a healthcare provider
to manage medications.
Conclusion
Renal disease is a serious condition that can have significant impacts on overall health. Recognizing symptoms and working with a healthcare provider to manage the condition is important in preventing further kidney damage. A nutritionist can also provide guidance on developing a healthy meal plan that supports kidney healt
Post a Comment
Post a Comment